Introduction
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious lung disease. It causes scarring in the lungs, making it hard to breathe. Many people want to know what pulmonary fibrosis is, what causes it, and how doctors diagnose it. In this blog, you will learn about the main causes, common symptoms, and the steps doctors take to find out if someone has this condition. Understanding pulmonary fibrosis can help you or your loved ones seek help early.
What Is Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis means the tissue in your lungs becomes thick and stiff. Because of this, your lungs cannot work as well as they should. Over time, it gets harder for oxygen to pass into your blood. As a result, you may feel short of breath. This disease can get worse slowly or quickly. Although there is no cure, early treatment can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. According to the American Lung Association, pulmonary fibrosis affects thousands of people each year.
Causes of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Many things can cause pulmonary fibrosis. Sometimes, doctors cannot find a clear reason. In these cases, it is called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, there are several known causes and risk factors:
Even though these are common causes, sometimes the reason remains unknown. Therefore, it is important to talk to your doctor if you notice any symptoms.
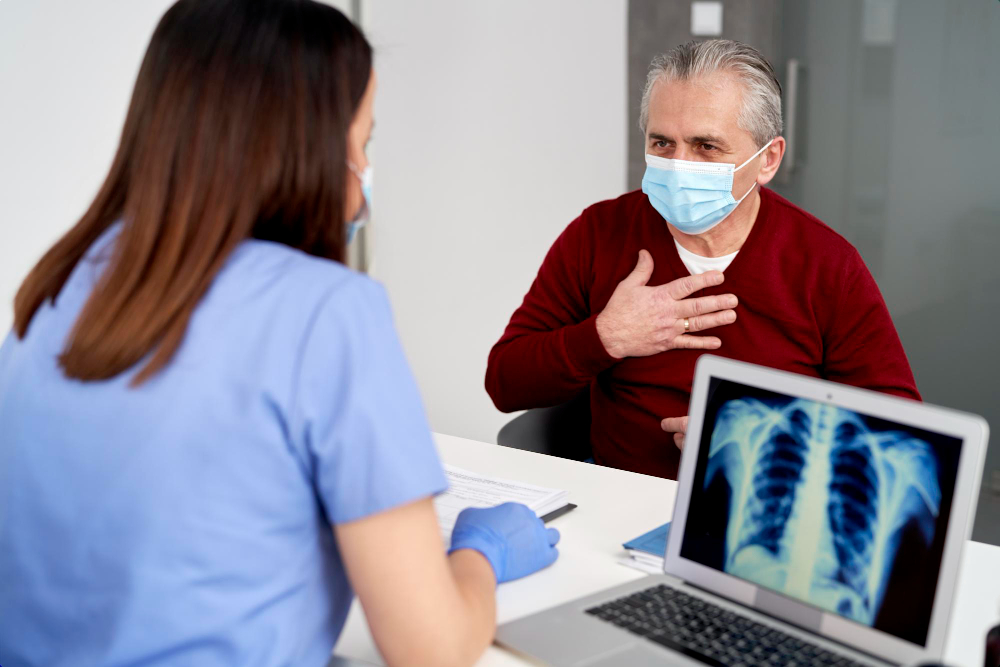
Symptoms of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis symptoms can be mild at first. Over time, they often get worse. Here are the most common signs:
If you notice these symptoms, you should see a doctor. Early diagnosis can help manage the disease better.
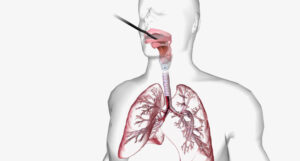
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Doctors use several tests to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may perform a physical exam. To confirm the diagnosis, doctors often use these tests:
Because some symptoms are like other lung diseases, these tests help doctors make the right diagnosis. According to the CDC, early diagnosis and treatment can slow the disease and improve life quality.
Conclusion
Pulmonary fibrosis is a serious lung disease that causes scarring and breathing problems. While the cause is sometimes unknown, many risk factors can increase your chances of getting it. If you notice symptoms like shortness of breath or a dry cough, do not wait. Consult a pulmonologist for personalized advice on pulmonary fibrosis. Early care can make a big difference.